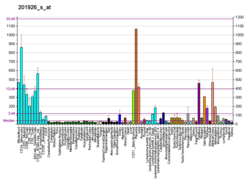
Decay-accelerating factor
| CD55 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | CD55, CR, CROM, DAF, TC, CD55 molecule (Cromer blood group), CHAPLE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 125240 MGI: 104849 HomoloGene: 479 GeneCards: CD55 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Complement decay-accelerating factor, also known as CD55 or DAF, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the CD55 gene.[5]
DAF regulates the complement system on the cell surface. It recognizes C4b and C3b fragments that are created during activation of C4 (classical or lectin pathway) or C3 (alternative pathway). Interaction of DAF with cell-associated C4b of the classical and lectin pathways interferes with the conversion of C2 to C2b, thereby preventing formation of the C4b2a C3-convertase, and interaction of DAF with C3b of the alternative pathway interferes with the conversion of factor B to Bb by factor D, thereby preventing formation of the C3bBb C3 convertase of the alternative pathway. Thus, by limiting the amplification convertases of the complement cascade, DAF indirectly blocks the formation of the membrane attack complex.[6]
This glycoprotein is broadly distributed among hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic cells. It is a determinant for the Cromer blood group system.
Structure
DAF is a 70 kDa membrane protein that attaches to the cell membrane via a glycophosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor.
DAF contains four complement control protein (CCP) repeats with a single N-linked glycan positioned between CCP1 and CCP2. CCP2, CCP3, CCP4 and three consecutive lysine residues in a positively charged pocket between CCP2 and CCP3 are involved in its inhibition of the alternate complement pathway. CCP2 and CCP3 alone are involved in its inhibition of the classical pathway.[7]
Pathology
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
Because DAF is a GPI-anchored protein, its expression is reduced in persons with mutations that reduce GPI levels such as those with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH). In PNH disorder, red blood cells with very low levels of DAF and CD59 undergo complement-mediated hemolysis. Symptoms include low red blood cell count (anemia), fatigue, and episodes of dark colored urine and other complications.[8]
Infectious diseases
DAF is used as a receptor by some coxsackieviruses and other enteroviruses.[9] Recombinant soluble DAF-Fc has been tested in mice as an anti-enterovirus therapy for heart damage;[10] however, the human enterovirus that was tested binds much more strongly to human DAF than to mouse or rat DAF. Echoviruses and coxsackie B viruses that use human decay-accelerating factor (DAF) as a receptor do not bind the rodent analogues of DAF.[11] and DAF-Fc has yet to be tested in humans.
Binding of DAF to human HIV-1 when the virons are budding from the surface of infected cells protects HIV-1 from complement mediated lysis.[12][13]
See also
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000196352 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000026401 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Medof ME, Lublin DM, Holers VM, Ayers DJ, Getty RR, Leykam JF, Atkinson JP, Tykocinski ML (April 1987). "Cloning and characterization of cDNAs encoding the complete sequence of decay-accelerating factor of human complement". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84 (7): 2007–11. Bibcode:1987PNAS...84.2007M. doi:10.1073/pnas.84.7.2007. PMC 304572. PMID 2436222.
- ^ "Molecular function for CD55 Gene".
- ^ Brodbeck WG, Kuttner-Kondo L, Mold C, Medof ME (Sep 2000). "Structure/function studies of human decay-accelerating factor". Immunology. 101 (1): 104–11. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2567.2000.00086.x. PMC 2327052. PMID 11012760.
- ^ Parker C, Omine M, Richards S, et al. (2005). "Diagnosis and management of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria". Blood. 106 (12): 3699–709. doi:10.1182/blood-2005-04-1717. PMC 1895106. PMID 16051736.
- ^ Karnauchow TM, Tolson DL, Harrison BA, Altman E, Lublin DM, Dimock K (August 1996). "The HeLa cell receptor for enterovirus 70 is decay-accelerating factor (CD55)". J. Virol. 70 (8): 5143–52. doi:10.1128/JVI.70.8.5143-5152.1996. PMC 190469. PMID 8764022.
- ^ Yanagawa B, Spiller OB, Choy J, Luo H, Cheung P, Zhang HM, Goodfellow IG, Evans DJ, Suarez A, Yang D, McManus BM (January 2003). "Coxsackievirus B3-associated myocardial pathology and viral load reduced by recombinant soluble human decay-accelerating factor in mice". Lab. Invest. 83 (1): 75–85. doi:10.1097/01.lab.0000049349.56211.09. PMID 12533688.
- ^ Spiller OB, Goodfellow IG, Evans DJ, Almond JW, Morgan BP (January 2000). "Echoviruses and coxsackie B viruses that use human decay-accelerating factor (DAF) as a receptor do not bind the rodent analogues of DAF". J. Infect. Dis. 181 (1): 340–3. doi:10.1086/315210. PMID 10608785. S2CID 31672193.
- ^ Marschang P, Sodroski J, Würzner R, Dierich MP (January 1995). "Decay-accelerating factor (CD55) protects human immunodeficiency virus type 1 from inactivation by human complement". Eur J Immunol. 25 (1): 285–90. doi:10.1002/eji.1830250147. PMID 7531147. S2CID 31079892.
- ^ Guibinga GH, Friedmann T (April 2005). "Baculovirus GP64-pseudotyped HIV-based lentivirus vectors are stabilized against complement inactivation by codisplay of decay accelerating factor (DAF) or of a GP64-DAF fusion protein". Mol Ther. 11 (4): 645–51. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2004.12.002. PMID 15771967.
Further reading
- Selinka HC, Wolde A, Sauter M, et al. (2004). "Virus-receptor interactions of coxsackie B viruses and their putative influence on cardiotropism". Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 193 (2–3): 127–31. doi:10.1007/s00430-003-0193-y. PMID 12920584. S2CID 21083098.
- Mikesch JH, Schier K, Roetger A, et al. (2007). "The expression and action of decay-accelerating factor (CD55) in human malignancies and cancer therapy". Cell. Oncol. 28 (5–6): 223–32. doi:10.1155/2006/814816. PMC 4618202. PMID 17167176.
External links
- Decay-Accelerating+Factor at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Cromer blood group system at BGMUT Blood Group Antigen Gene Mutation Database at NCBI, NIH
- Overview of all the structural information available in the PDB for UniProt: P08174 (Complement decay-accelerating factor) at the PDBe-KB.
- v
- t
- e
-
 1h03: HUMAN CD55 DOMAINS 3 & 4
1h03: HUMAN CD55 DOMAINS 3 & 4 -
 1h04: HUMAN CD55 DOMAINS 3 & 4
1h04: HUMAN CD55 DOMAINS 3 & 4 -
 1h2p: HUMAN CD55 DOMAINS 3 & 4
1h2p: HUMAN CD55 DOMAINS 3 & 4 -
 1h2q: HUMAN CD55 DOMAINS 3 & 4
1h2q: HUMAN CD55 DOMAINS 3 & 4 -
 1nwv: SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF A FUNCTIONALLY ACTIVE COMPONENT OF DECAY ACCELERATING FACTOR
1nwv: SOLUTION STRUCTURE OF A FUNCTIONALLY ACTIVE COMPONENT OF DECAY ACCELERATING FACTOR -
 1ojv: DECAY ACCELERATING FACTOR (CD55): THE STRUCTURE OF AN INTACT HUMAN COMPLEMENT REGULATOR.
1ojv: DECAY ACCELERATING FACTOR (CD55): THE STRUCTURE OF AN INTACT HUMAN COMPLEMENT REGULATOR. -
 1ojw: DECAY ACCELERATING FACTOR (CD55): THE STRUCTURE OF AN INTACT HUMAN COMPLEMENT REGULATOR.
1ojw: DECAY ACCELERATING FACTOR (CD55): THE STRUCTURE OF AN INTACT HUMAN COMPLEMENT REGULATOR. -
 1ojy: DECAY ACCELERATING FACTOR (CD55): THE STRUCTURE OF AN INTACT HUMAN COMPLEMENT REGULATOR.
1ojy: DECAY ACCELERATING FACTOR (CD55): THE STRUCTURE OF AN INTACT HUMAN COMPLEMENT REGULATOR. -
 1ok1: DECAY ACCELERATING FACTOR (CD55): THE STRUCTURE OF AN INTACT HUMAN COMPLEMENT REGULATOR.
1ok1: DECAY ACCELERATING FACTOR (CD55): THE STRUCTURE OF AN INTACT HUMAN COMPLEMENT REGULATOR. -
 1ok2: DECAY ACCELERATING FACTOR (CD55): THE STRUCTURE OF AN INTACT HUMAN COMPLEMENT REGULATOR.
1ok2: DECAY ACCELERATING FACTOR (CD55): THE STRUCTURE OF AN INTACT HUMAN COMPLEMENT REGULATOR. -
 1ok3: DECAY ACCELERATING FACTOR (CD55): THE STRUCTURE OF AN INTACT HUMAN COMPLEMENT REGULATOR.
1ok3: DECAY ACCELERATING FACTOR (CD55): THE STRUCTURE OF AN INTACT HUMAN COMPLEMENT REGULATOR. -
 1ok9: DECAY ACCELERATING FACTOR (CD55): THE STRUCTURE OF AN INTACT HUMAN COMPLEMENT REGULATOR.
1ok9: DECAY ACCELERATING FACTOR (CD55): THE STRUCTURE OF AN INTACT HUMAN COMPLEMENT REGULATOR. -
 1uot: HUMAN CD55 DOMAINS 3 & 4
1uot: HUMAN CD55 DOMAINS 3 & 4 -
 1upn: COMPLEX OF ECHOVIRUS TYPE 12 WITH DOMAINS 3 AND 4 OF ITS RECEPTOR DECAY ACCELERATING FACTOR (CD55) BY CRYO ELECTRON MICROSCOPY AT 16 A
1upn: COMPLEX OF ECHOVIRUS TYPE 12 WITH DOMAINS 3 AND 4 OF ITS RECEPTOR DECAY ACCELERATING FACTOR (CD55) BY CRYO ELECTRON MICROSCOPY AT 16 A